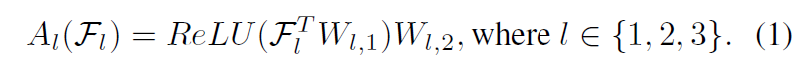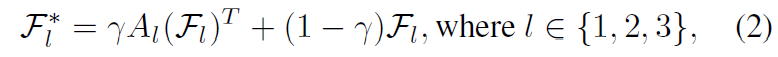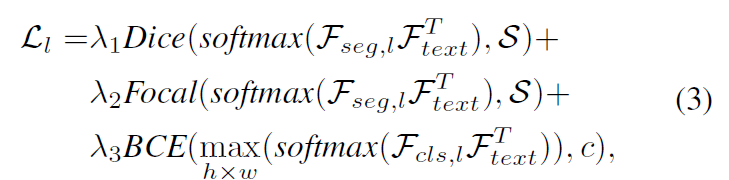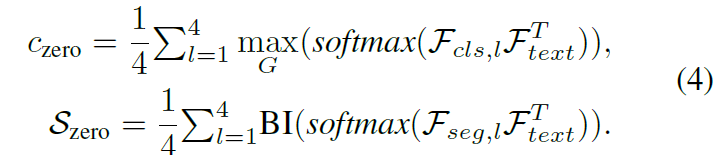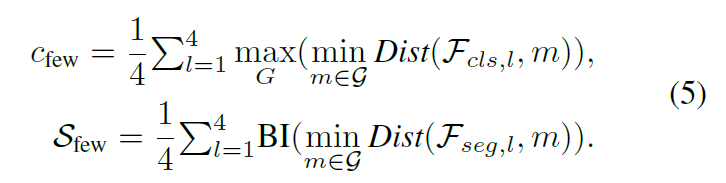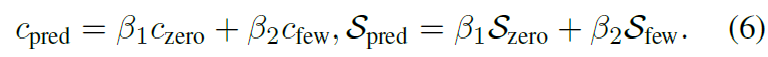Adapting Visual-Language Models for Generalizable Anomaly Detection in Medical Images
Adapting Visual-Language Models for Generalizable Anomaly Detection in Medical Images
CVPR 2024 Highlight, 2024-08-16 기준 6회 인용
Task
- Anomaly Detection
- CLIP
Contributions
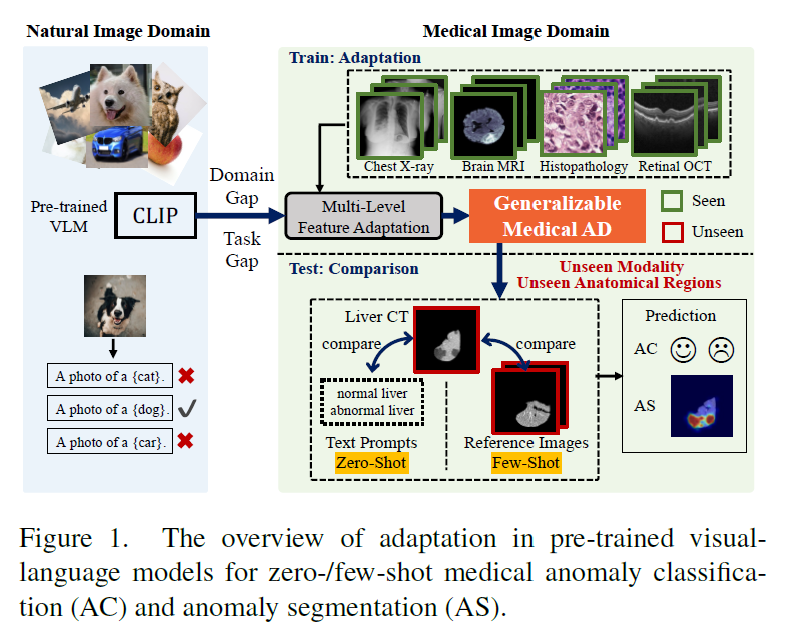
- Visual-language pre-trained models (CLIP) 을 활용하여 Anomaly Detection 하는 방법 제안
- Lightweight multi-level adaptation 을 통해서 medical data 에 대한 domain gap, task gap 에 대해서 alingment
- zero-shot, few-shot 세팅해서 좋은 성능을 보여줌
Proposed Method
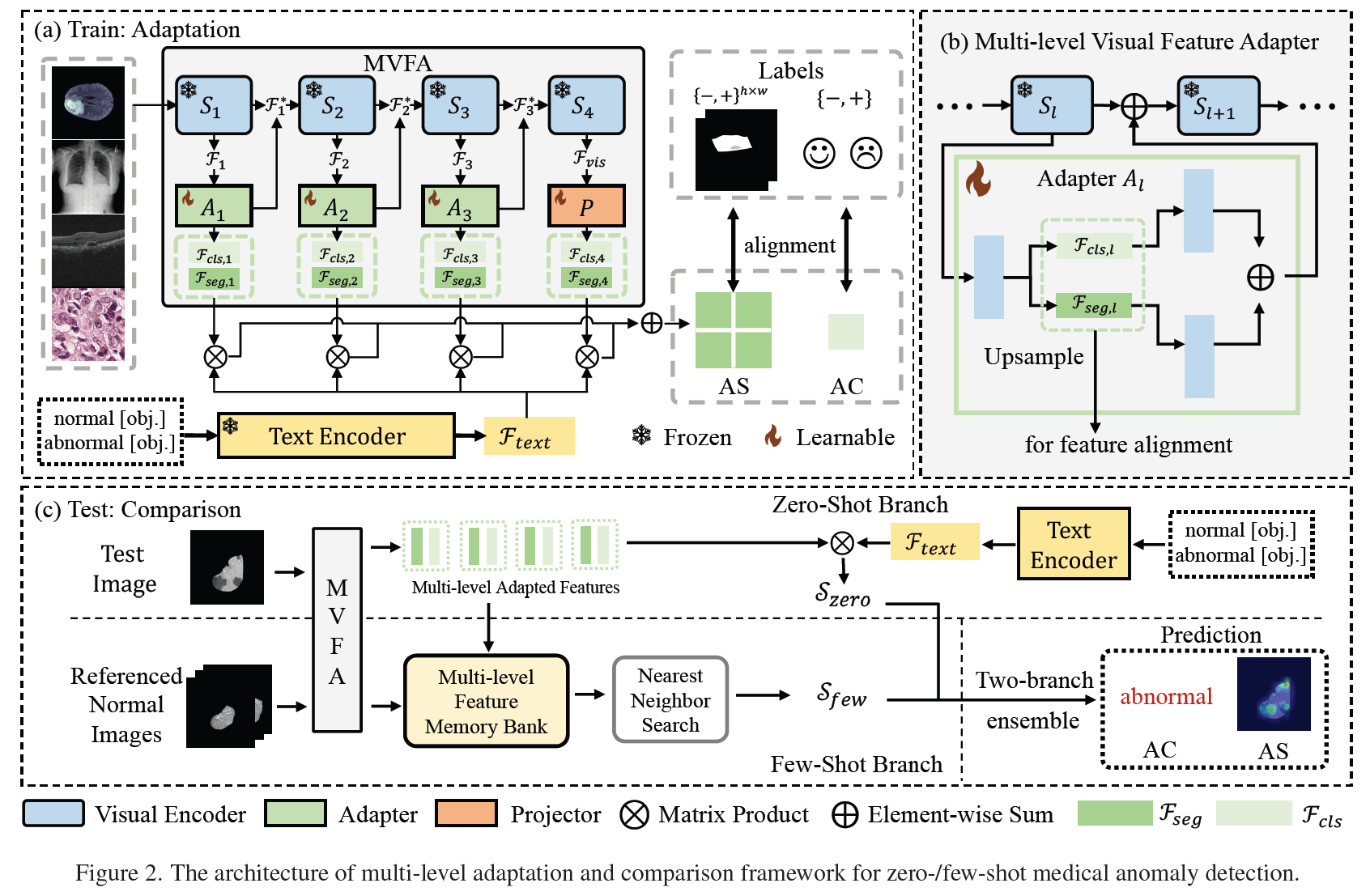
CLIP 모델로 부터 Featrue extraction 하고 train set 으로 adaptation 하는 concept
Train: Multi-Level Feature Adaptation
Multi-level Visual Feature Adapter (MVFA)
small set of learnable bottleneck linear layers 을 사용해서 feature adaptation
두개의 linear layers 사용
다음 encoder stage 로 넘겨줄때 기존의 feature와 adaptation 된 feature 를 수식 (2) 와 같이 계산
adaptation 을 진행할 때 classification, segmentation 을 나누어서 진행
classification 과 segmentation을 하기 위한 adaptor 와 optimizer 가 각각 따로 존재
Language Feature Formatting
normal, abnormal 에 대한 text templates 를 만들어서 text feature 를 생성
Visual-Language Feature Alignment
각 stage 별로 segmentation, classification loss 를 연산하고 합산
text feature 와의 similarity 를 기반으로 연산
Test: Multi-Level Feature Comparison
Zero-Shot Branch
각 stage 별로 text feature 와의 similarity 로 zero-shot branch 의 score 값들을 연산
Few-Shot Branch
Few-shot 으로 학습때 사용한 normal 이미지들에 대한 memory bank feature 와의 거리를 기반으로 score 계산
Zero-shot branch 와 Few-shot branch 에서 구해진 score 들을 각각 더해서 최종 predictions 계산
Experimental Results
Medical domain 에 대해서 Few-shot 으로 학습한 실험 결과
코드를 확인해보았을 때 normal 이미지 K장, abnormal 이미지 K장 사용한 것으로 확인
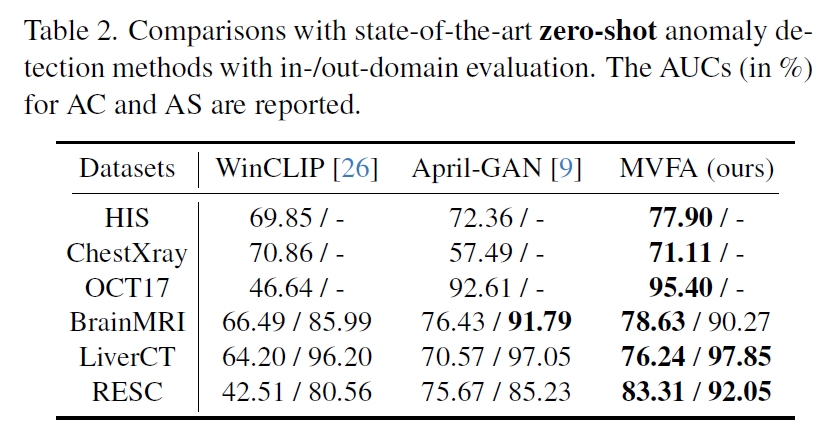
Zero-shot 으로 학습한 실험 결과
평가하고자 하는 dataset 제외하고 나머지 dataset 을 train set 으로 사용
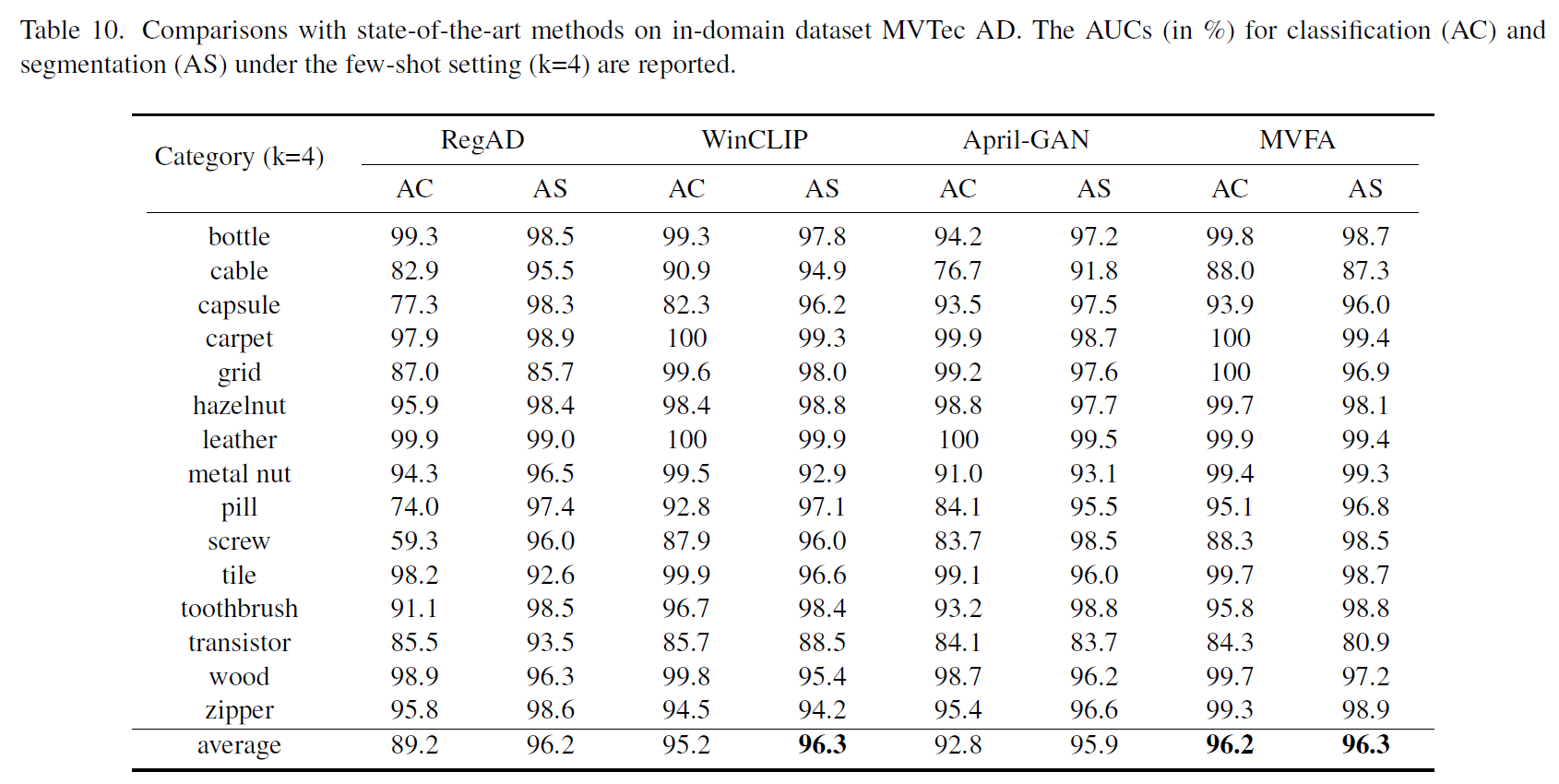
industrial anomaly detection (MVTec) 에 대한 실험 결과
논문과 코드에는 명확한 설명이 없지만 Medical domain 에 대해서 구현된 코드를 확인하여 추측
- category 하나당 모델 하나 학습
- normal 이미지 K 장만 사용해서 학습?